Time-Sensitive Networking - Part 1
Today I am going to talk about what I have been researching for the past couple of months 😉.
Imagine one of your family members living in a remote area for work, and they encounter a severe medical emergency. They need urgent surgery, but there is no specialized surgeon nearby. Their only hope is a remote surgical procedure facilitated by telemedicine. Thanks to TSN, robotic surgical instruments replicate their movements in real-time, allowing them to operate with astonishing accuracy, just as if they were physically present. High-definition video streaming is another lifesaving aspect of TSN in the surgery. The surgeons need a precise, uninterrupted video feed to guide them through the intricate procedure. Without this, there could be disastrous consequences.
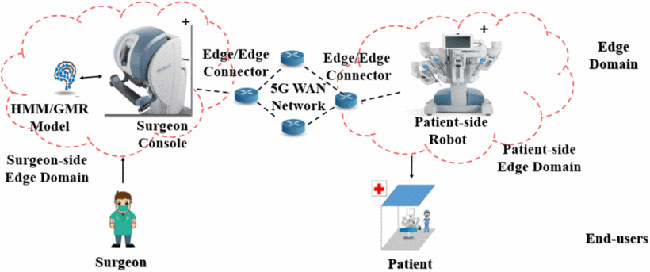
*Telemedicine [1]*
Now, let’s change the scenario and go to a bustling industrial automation and manufacturing plant where precision and coordination are paramount. The plant, specializing in producing high-end electronics, is known for its cutting-edge automation systems. The intricate dance of robotic arms, conveyor belts, and assembly stations is a marvel to behold. One day, a massive rush of orders comes in, pushing the plant’s production capacity to the limit. This unexpected surge would throw most facilities into chaos, but not this one. Thanks to TSN, synchronized robotics is a given. Robotic arms weld, paint, and assemble with sub-millisecond precision. The production line maintains its pace, unaffected by the added pressure.
Quality control is of utmost importance. Cameras and sensors dot the assembly line, capturing real-time data for inspections.
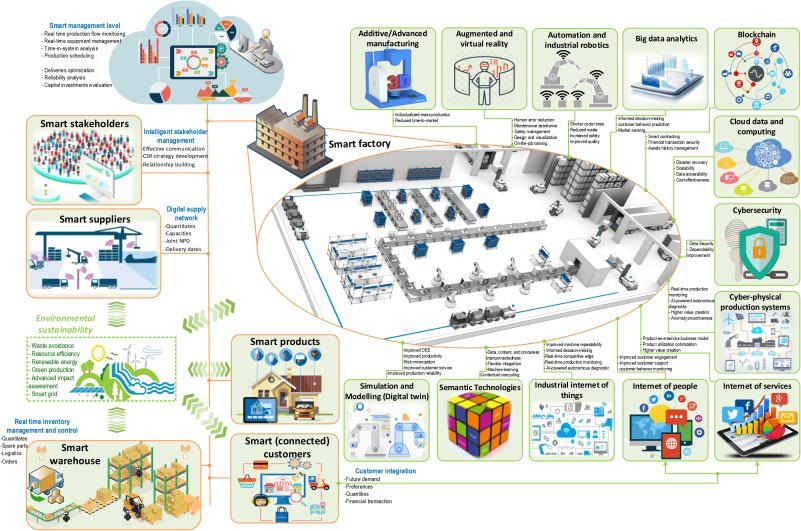
*Industry 4.0 [2]*
Safety is never compromised. TSN is instrumental in managing and distributing safety-critical information throughout the plant. Emergency stop signals, collision avoidance alerts, and other safety-related messages are communicated with minimal latency, ensuring the protection of the workforce.
Even equipment maintenance is streamlined. Predictive maintenance systems rely on TSN to provide real-time data on machinery performance. Any sign of wear or impending failure is instantly reported, allowing for proactive maintenance, avoiding costly breakdowns and downtime.
SO what is TSN ? 🤠
IEEE 802.1 Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) is a set of standards and tools that uses Ethernet to achieve real-time deterministic communications with low latency and high reliability
The TSN technology is based on four basic key concepts, accurate time synchronization, bounded guaranteed low latency, ultra reliability and resource management.
I will dive into the technical details of TSN including challenges, in the next parts. Stay tuned 😇
References:
[1] F. Boabang, A. Ebrahimzadeh, R. H. Glitho, H. Elbiaze, M. Maier and F. Belqasmi, “A Machine Learning Framework for Handling Delayed/Lost Packets in Tactile Internet Remote Robotic Surgery,” in IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 4829-4845, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2021.3106577.
[2] M. Ghobakhloo, “Industry 4.0, Digitization, and Opportunities for Sustainability,” in Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 252, 2020, pp. 119869, ISSN 0959-6526, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119869.